What is the thyroid?`
Thyroid is a small gland located in the lower part of your neck. It produces hormones that play a major role in your metabolism and energy. An estimated 20 million Americans have thyroid disorder, and the majority are unaware of their condition. Women are five to eight times more than men, over 12 percent of the U.S. population will develop a thyroid condition during their lifetime, About 4.6 percent of the U.S. population age 12 and older has hypothyroidism.
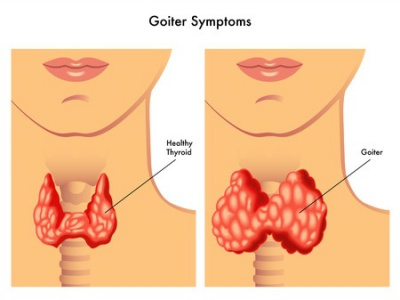
What is thyroid goiters?
A goiter is an abnormally large thyroid gland. A goiter develops either because the whole gland is swollen or the gland has multiple growths or nodules on it. While some people with a goiter have no symptoms, others may have symptoms of an overactive or underactive thyroid.
Hyperthyroid: is the medical term for an overactive thyroid, which produces too much thyroid hormone. Symptoms may include: Anxiety, rapid heart rate, diarrhea, weight loss.
Hypothyroidism: refers to an underactive thyroid, which products too little thyroid hormone. Symptoms may include: Depression, fatigue, constipation, weight gain.
What Causes a Goiter?
- Iodine deficiency— A goiter may be caused by not getting enough iodine through the foods you eat. However, it is rare in the United States, because table salt is supplemented with iodine.
- Graves’ disease— This autoimmune disorder causes hyperthyroidism. Grave’s disease causes the body to produce a protein called thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin that mistakenly attacks the thyroid, causing it to overproduce thyroid hormones and swell in size.
- Hashimoto’s disease— This is another autoimmune disorder in which antibodies damage thyroid cells, leaving fewer cells to produce thyroid hormones. The pituitary gland, which controls your thyroid, stimulates the thyroid to produce more hormones, making the thyroid swell. Hashimoto’s disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
- Thyroid nodules— Nodules are overgrowths of tissue that may overproduce thyroid hormone or many not cause any symptoms. Rarely, nodules may contain cancer cells.
- Thyroiditis— This condition is an inflammation of the cells in the thyroid that may cause the thyroid to produce too much or too little thyroid hormone.
- Thyroid cancer— Cancerous cells may grow in nodules on the thyroid.
What is Hashimoto’s Disease?
Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It also is called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis ( inflammation of the thyroid gland), which is known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis or autoimmune thyroiditis, affects 14 million people in the United States.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is named after the Japanese surgeon who discovered it in 1912. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means it occurs when immune cells attack healthy tissue instead of protecting it. In the case of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, immune cells mistakenly attack healthy thyroid tissue, causing inflammation of the thyroid. Autoimmune diseases affect women more than men, and women are 7 times more likely to have Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
When your thyroid gland comes under attack from malfunctioning immune cells, it impairs your thyroid’s ability to make thyroid hormone. This can result in hypothyrodism. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
If Hashimoto’s thyroiditis attacks your thyroid to the point that the gland can no longer produce enough thyroid hormones for your body to function properly, then you will develop hypothyroidism.
But hypothyroidism isn’t the only complication associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. In some people, the disorder causes the thyroid to become so inflamed and enlarged that is goiter develops.
For people who develop symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, such as hypothyroidism or goiter, thyroid hormone therapy is needed.
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is when your thyroid does not make enough thyroid hormones. It is also called underactive thyroid. This slows down many of your body’s functions, like your metabolism.
The most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States is Hashimoto’s disease. In people with Hashimoto’s disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid. This attack damages the thyroid so that it does not make enough hormones.
Hyperthyroidism treatment (radioiodine)Hypothyroidism also can be caused by:
- Radiation treatment of certain cancers
- Thyroid removal
- Some medication
What is Symptoms of Hypothyroidism ?
When the thyroid gland is underactive, your metabolism slows down and you suffer from symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight gain
- Constipation
- Dry skin and hair
- Hair Loss
- Puffiness or swelling in the face
- Muscle aches and weakness
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Brittle hair and nails
- Depression
- Cold intolerance
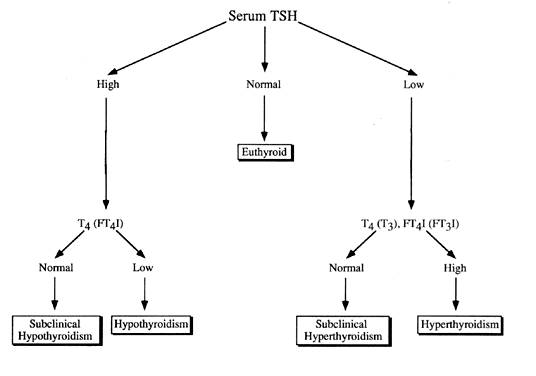
What is Lab testing?